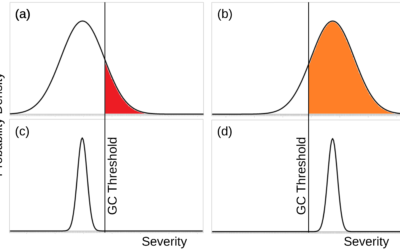
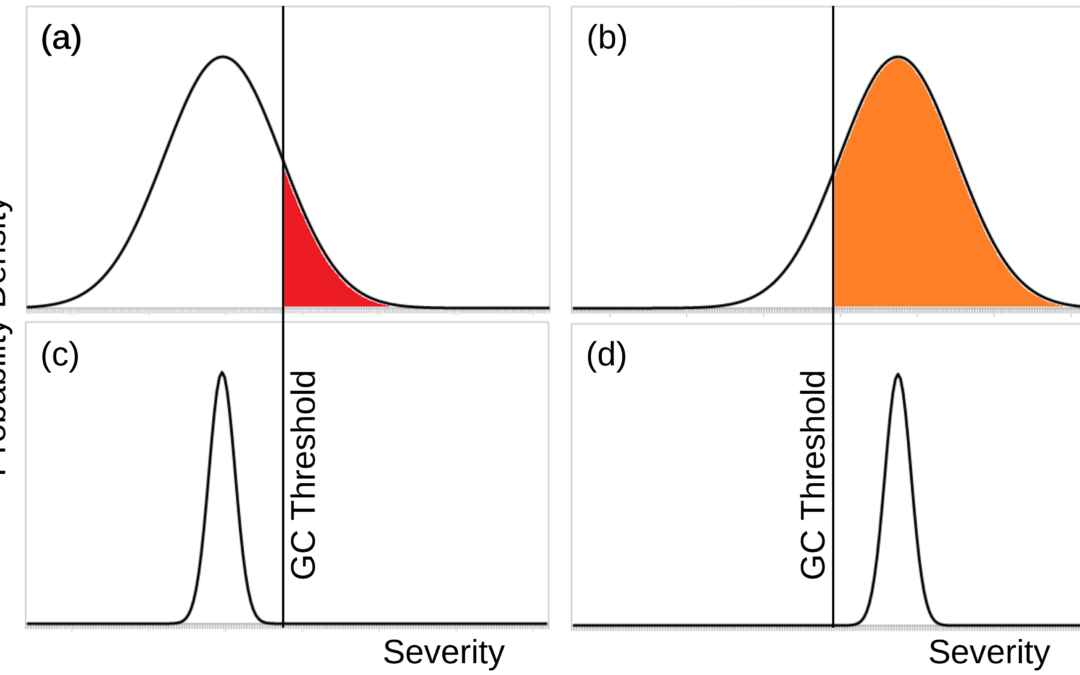
On 17 March 2014, Kungliga Vetenskapsakademien (KVA, the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences) is hosting an event Emerging technologies and the future of humanity. I will give a talk “The great downside dilemma for risky emerging technologies”, loosely based on themes from my recent paper Double catastrophe: Intermittent stratospheric geoengineering induced by societal collapse. Usually I try to avoid travel like this, but this is a good event and they wouldn’t let me present remotely. Here’s my abstract:
The great downside dilemma for risky emerging technologies
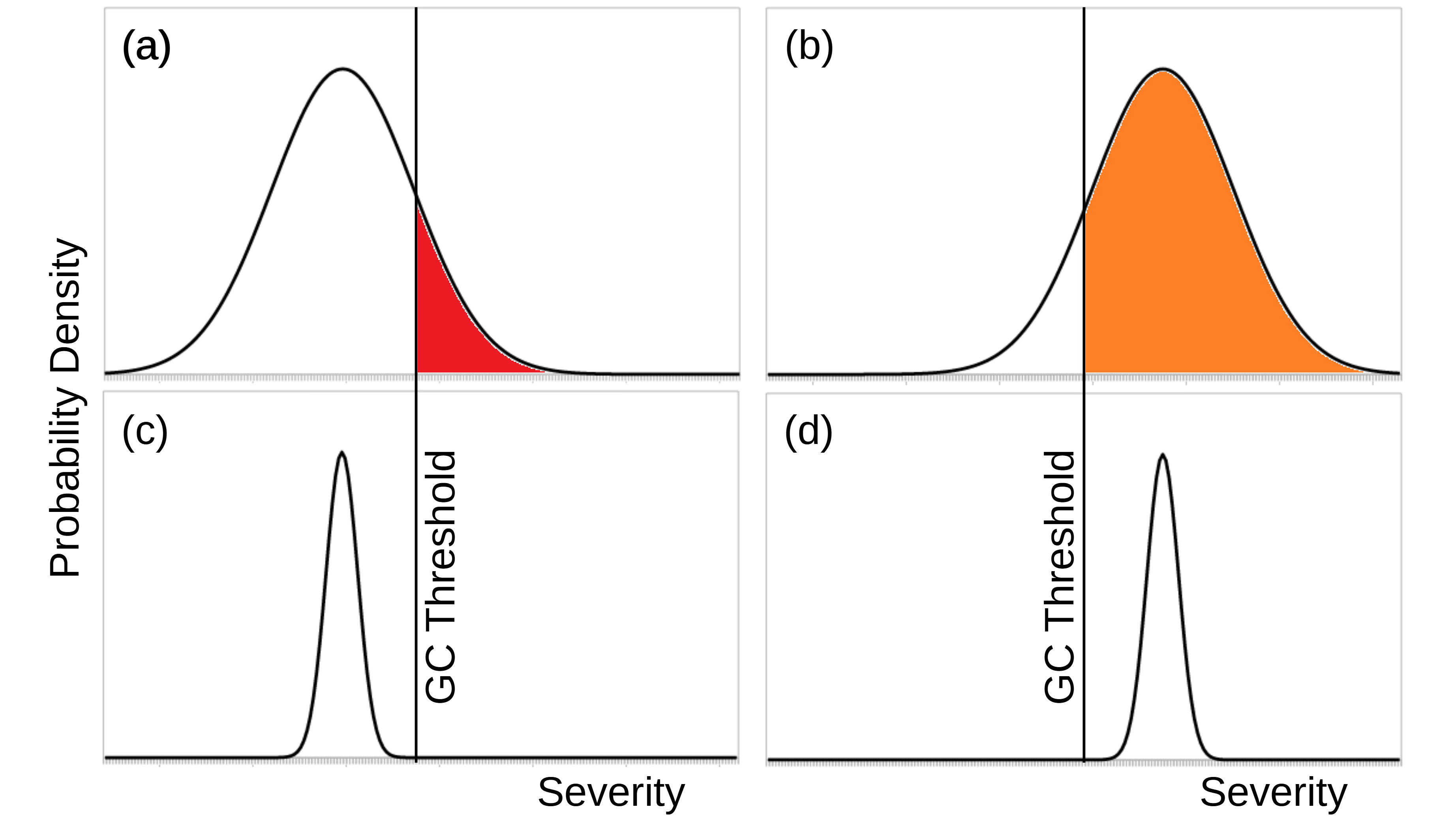
Many emerging technologies show potential to solve major global challenges, but some of these technologies come with possible catastrophic downsides. In this talk I will discuss the great dilemma that these technologies pose: should society accept the risks associated with using these technologies, or should it instead accept the burdens that come with abstaining from them? I will use stratospheric aerosol geoengineering as an illustrative example, which could protect humanity from many burdens of global warming but could also fail catastrophically. Other technologies that pose this great downside dilemma include certain forms of biotechnology, nanotechnology, and artificial intelligence, whereas nuclear fusion power shows less downside.