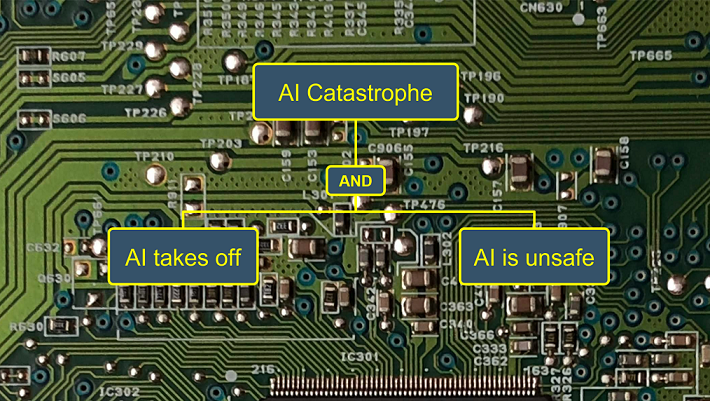
Artificial superintelligence (ASI) is artificial intelligence (AI) with capabilities that are significantly greater than human capabilities across a wide range of domains. A hallmark of the ASI issue is disagreement among experts. This paper demonstrates and discusses methodological options for modeling and interpreting expert disagreement about the risk of ASI catastrophe. Using a new model called ASI-PATH, the paper models a well-documented recent disagreement between Nick Bostrom and Ben Goertzel, two distinguished ASI experts. Three points of disagreement are considered: (1) the potential for humans to evaluate the values held by an AI, (2) the potential for humans to create an AI with values that humans would consider desirable, and (3) the potential for an AI to create for itself values that humans would consider desirable. An initial quantitative analysis shows that accounting for variation in expert judgment can have a large effect on estimates of the risk of ASI catastrophe. The risk estimates can in turn inform ASI risk management strategies, which the paper demonstrates via an analysis of the strategy of AI confinement. The paper find the optimal strength of AI confinement to depend on the balance of risk parameters (1) and (2).
Academic citation:
Seth D. Baum, Anthony M. Barrett, and Roman V. Yampolskiy, 2017. Modeling and interpreting expert disagreement about artificial superintelligence. Informatica, vol. 41, no. 4 (December), pages 419-427.
Image credit: Aler Kiv
This blog post was published on 28 July 2020 as part of a website overhaul and backdated to reflect the time of the publication of the work referenced here.