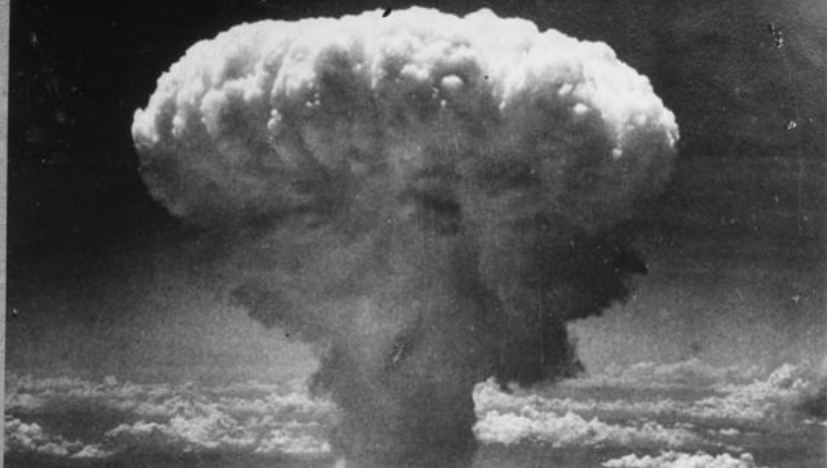
Nuclear weapons explosions send large quantities of smoke high into the atmosphere. The smoke blocks incoming sunlight and destroys ozone, causing major environmental harms worldwide, including cold temperatures, reduced precipitation, and increased ultraviolet radiation. In technical terms, nuclear winter refers to cooling such that winter-like temperatures occur during summer, as caused by nuclear war. This paper uses the term nuclear winter more generally to refer to the full set of global environmental harms from nuclear war. The purpose of the paper is to survey the many ways of reducing either the probability or the severity of nuclear winter. A core point is that many actions can be taken by many different people, possibly including everyone alive around the world.
Reducing the probability of nuclear war. Nuclear winter cannot happen without a sizable nuclear war. There are several ways to reduce the probability of nuclear war. Diplomacy helps defuse tensions between nuclear-armed countries. It can be conducted by professional diplomats, researchers (“Track II Diplomacy”), and even ordinary citizens. Weapons systems can be designed to make it less likely that nuclear weapons are used, for example by designing warning systems to avoid false alarms or by designing delivery systems to survive incoming attacks. Doctrine can be written to reduce the range of scenarios in which countries would resort to using nuclear weapons, for example by insisting that nuclear weapons would only be used in retaliation against someone else’s nuclear attack. Complete and permanent disarmament would ensure that there are no nuclear weapons ever, in which case nuclear war could not occur.
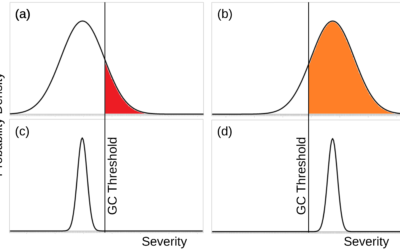
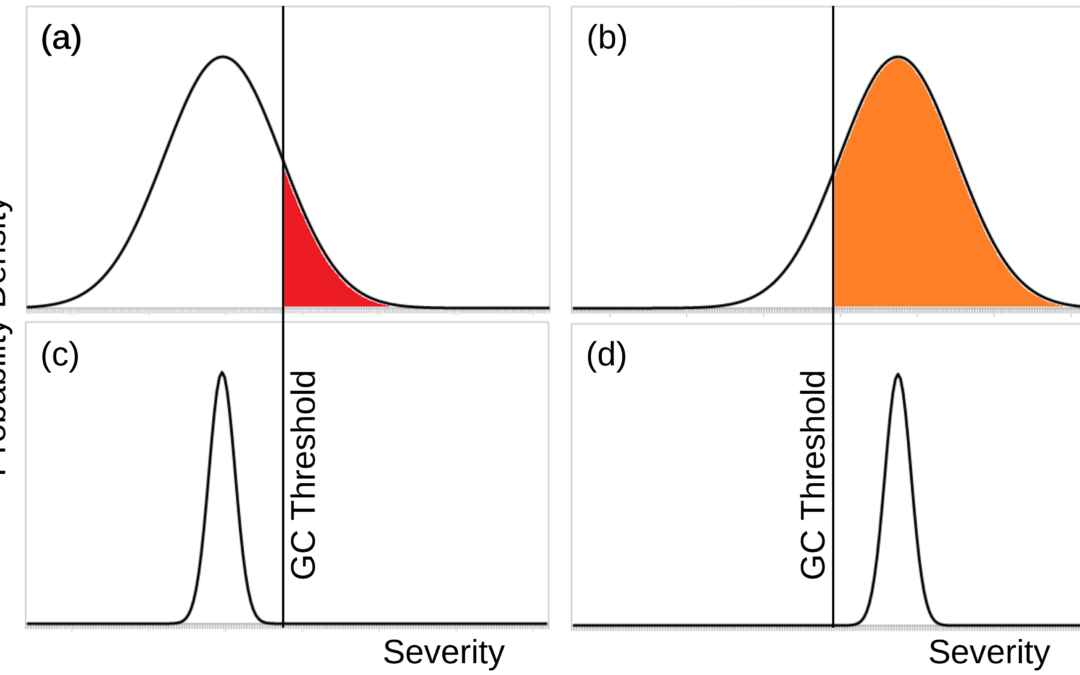
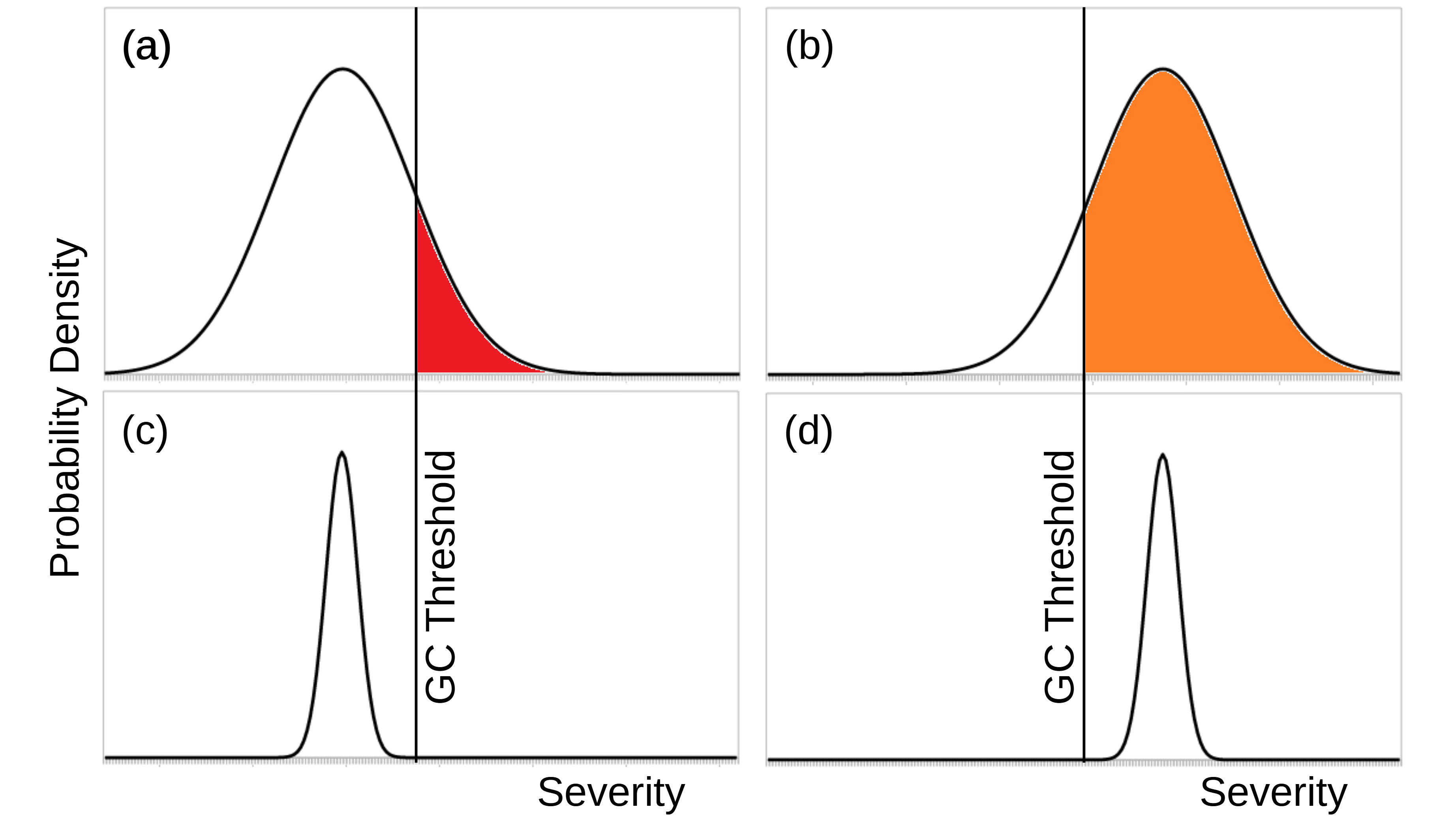
Reducing the severity of nuclear winter. If a nuclear war occurs, there are several ways to make its global environmental consequences less severe. Targeting means detonating nuclear weapons at locations that produce less smoke, in particular by avoiding cities. A no-cities targeting policy would also reduce civilian casualties, though it could also make nuclear war more probable by making deterrence less effective. Partial disarmament reduces the number of nuclear weapons that can be used in a war. Nuclear war timing would postpone nuclear wars when there is already a lot of smoke in the atmosphere, such as after a volcano eruption or another nuclear war. Such postponement is unlikely in practice.
Increasing resilience to nuclear winter. Given a nuclear winter of a certain environmental severity, several things can be done to help the human survivors. Resource stockpiles prepared before the war provide food and other critical resources. Large stockpiles would be needed, because nuclear winter could last 10-20 years. Refuges and space colonies offer places for people to live that would be unaffected by the nuclear winter. Alternative food is a new proposal to produce food from other energy sources without sunlight.
Indirect interventions. Finally, several things can be done that would help advance the actions described above. Research can improve decision making on any of the actions. Social science and policy research could be especially valuable. Raising awareness would get more people engaged in efforts to confront nuclear winter. Prominent non-governmental organizations make it easy for citizens to get involved. Providing funding would enable more people to work on some of the actions to confront nuclear winter.
Academic citation:
Seth D. Baum, 2015. Confronting the threat of nuclear winter. Futures, vol. 72 (September), pages 69-79, DOI 10.1016/j.futures.2015.03.004.
Download Preprint PDF • View in Futures
Image credit: United States Office of War Information
This blog post was published on 28 July 2020 as part of a website overhaul and backdated to reflect the time of the publication of the work referenced here.